Background: The current evidence suggests that inflammatory phenotype contributes to the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). While our understanding of complement cascade contributions to inflammation-mediated pathologies has expanded, role this cascade plays in etiology of myeloid malignancies has not been detailed. Previously, we uncovered an inactivating RNSV in complement factor I (CFI G119R), an inhibitor of the complement cascade, in 20% of PMF patients (n=10) using WGS, and in a separate patient cohort (n=10) we observed an increase in CH50 levels (n=3) and decrease in C3 levels (n=3) (Oakes et al., 2021, Blood, 138:1472).These findings prompted us to generate murine models allowing assessment of the Cfi loss-driven complement overactivity effects on hematopoiesis and development of MPNs.
Methods: A conventional Cfi knockout (KO) mouse model was generated by targeting exon 2 of the Cfi gene using CRISPR/Cas9. Inactivation of one or two copies of Cfi was confirmed by genotyping and total loss (Cfi KO) or Cfi deficiency (Cfi HET) were confirmed in peripheral blood (PB) plasma. Complete blood counts (CBC) and the frequencies of granulocytes, B cells, plasmocytes, T cells, macrophages/monocytes, platelets, erythroid cells in the bone marrow were longitudinally assessed by flow cytometry for 40 weeks in Cfi WT, HET and KO mice. Cfi HET animals were crossed with JAK2V617F(fl/+);Mx1-cre(+) mice (obtained from crossing B6.Cg-Tg( Mx1- cre+ 1)Cgn/J; # 003556, JAX) and JAK2V617F expressing (B6N.129S6(SJL)- Jak2 tm1.2Ble/AmlyJ #031658, JAX) to generate Cfi(+/-)/JAK2V617F(fl/+);Tg(Mx1-cre(+/-) (CFI/JAK2) strain. Complete blood counts and survival were monitored for Cfi(+/+)/JAK2V617F(fl/+);Tg(Mx1-cre)(+/-) (CFI WT/JAK2 HET) Cfi(+/-)/JAK2V617F(fl/+);Tg(Mx1-cre)(+/-) (CFI HET/JAK2 HET) or Cfi(-/-)/JAK2V617F(fl/+); Tg(Mx1-cre)(+/-) (CFI KO/JAK2 HET) mice.
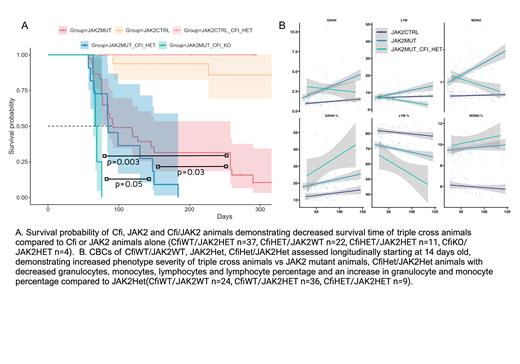
Results:Cfi HET and KO mice were fertile and viable. Cohort of Cfi WT n=13, Het n=12, KO n=13 mice was subjected to analyses. Genotypes were confirmed via PCR and western blot. Flow cytometry demonstrated a copy loss dependent decrease in total T-cells (CD3+) and increase in mature resting B-cells (CD19+/B220+). CBC demonstrated a copy loss dependent decrease in both monocyte (p adj. KO vs. WT 0.002) and granulocyte percentage (p adj. KO vs. WT 0.003), and increase in lymphocyte percentage (p adj. KO vs. WT 0.001). In PB plasma we detected increased C3 activation in KO mice compared to WT and Het, demonstrated as decreased C3 alpha and presence of inactivated C3 due to increased proteolytical processing of C3 complex. Proteolytic cleavage of CFB compared to Cfi WT and Het was also noted in Cfi KO animals. A significant decrease in survival probability of CFI HET/JAK2 HET vs. CFI WT/JAK2 HET (p=0.03), CFI KO/JAK2 HET vs. CFI WT/JAK2 HET (p=0.003), and CFI HET/JAK2 HET vs. CFI KO/JAK2 HET (p=0.05) averaging 92 days for Cfi HET/JAK2 HET, 67 days for Cfi KO/JAK2 HET vs. 98 days for Cfi WT/JAK2 HET was noted (Fig. A). A granulocyte and monocyte percentage of CFI HET/JAK2 HET was increased as compared to CFI WT/JAK2 HET mice (Fig. B).
Conclusions:An overactivation of complement cascade at the C3 level is noted in Cfi deficient animals, that is phenotypically linked to an increase in frequency of B cells. These findings may suggest involvement of Cfi directly, and/or in conjunction with generally overactive complement, in B-cell maturation and function. The absence of one copy of Cfi in JAK2V617F mice shows more severe MPN disease progression resulting in markedly decreased survival, linked to increased frequencies of monocytes and granulocytes and markedly decreased lymphocytes. In sum, these data indicate that increased complement activity may increase JAK2V617F-dependent phenotype severity. In depth mechanistic studies detailing observed phenotype are warranted.
Disclosures
Reagan:Pfizer: Research Funding; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Olszewski:Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, Genetech, Inc. / F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Precision Biosciences, Genmab: Research Funding; Genmab, Blue Cross/Blue Shield of Rhode Island, Schrodinger, ADC Therapeutics, BeiGene: Consultancy.